Abstract

Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) may arise from precursor B or T cells (BCP- and T-ALL, respectively) and treatment is based on polychemotherapy. There is an urgent need for novel immunotherapy targets to reduce therapy toxicity and to target relapsed/refractory (r/r) disease, especially in T-ALL where immunotherapy approaches are scarce.
The Interleukin-7-receptor (IL7R) has been shown to play a pivotal role in the development of both BCP-ALL and T-ALL (Geron et al. 2022; Silva et al. 2022). The IL7Rα-chain (CD127)-targeting antibody OSE-127 has a good safety profile in healthy volunteers (NCT03980080) and has entered phase 2 trials in Ulcerative Colitis (NCT04882007) and Sjögren's syndrome (NCT04605978). We previously reported high preclinical efficacy of OSE-127 in BCP-ALL patient derived xenograft (PDX) models of different cytogenetic backgrounds (Lenk and Baccelli et al. ASH, 2021). However, the preclinical efficacy of OSE-127 in T-ALL had not yet been investigated and the mechanism of action underlying its anti-leukemic efficacy remained unclear.
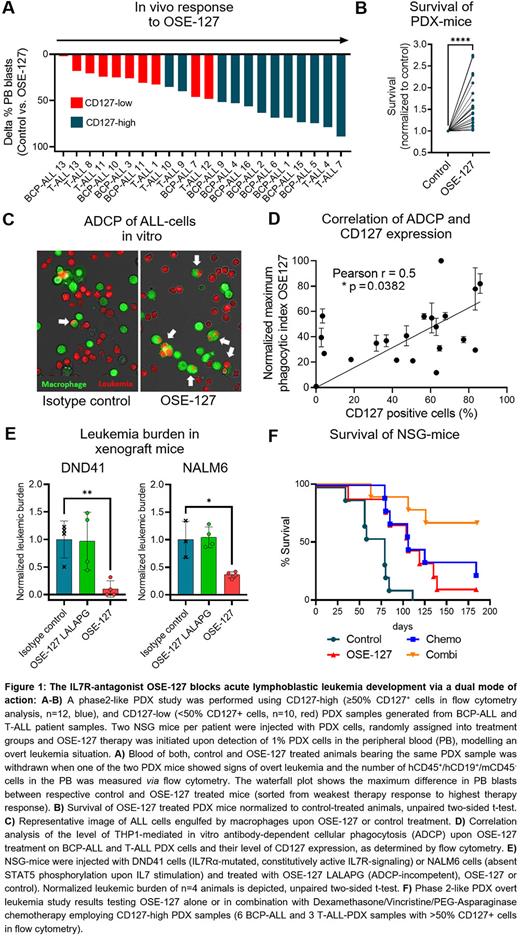
First, we investigated the in vivo efficacy of OSE-127 treatment on BCP-ALL and T-ALL cells by conducting a preclinical phase 2-like PDX study. Two NSG mice per patient were injected with BCP-ALL (n=13) or T-ALL (n=9) PDX cells (including 7 r/r ALL samples), randomly assigned into treatment groups and OSE-127 therapy was initiated when 1% leukemic blasts were detected in the peripheral blood (PB). OSE-127 treated mice showed a reduction of PB blasts in 21/22 (95%) PDX samples in vivo when the corresponding control mice showed clinical signs of overt leukemia (Figure 1A). This translated into a 1.6-fold prolongation of median survival (MS) of OSE-127 treated PDX mice (P<0.0001, Figure 1B). Of note, blast reduction strongly correlated with CD127 expression levels in the samples (Pearson r=0.5372, P=0.0099).
Next, we characterized the mode of action of OSE-127. As expected, OSE-127 blocked STAT5 phosphorylation in IL7-dependent ALL cell lines and PDX samples. As OSE-127 is not internalized by CD127 expressing cells (Belarif et al. 2018), we investigated whether OSE-127 might also exert immune-mediated effects. We found that OSE-127 did not promote antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), but efficiently induced macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) in BCP- and T-ALL cell lines and PDX cells in vitro, in a manner dependent on CD127 expression levels (Pearson r=0.5000, P=0.0352, Figure 1C-D). In line with these observations, inactivating mutations of the Fc fraction of OSE-127 (OSE-127-LALAPG) prevented ADCP of ALL cells in vitro, while conserving its antagonistic properties on IL7R signaling. To further evaluate the contribution of ADCP to the anti-leukemic activity of OSE-127, we compared the in vivo efficacy of OSE-127 and OSE-127-LALAPG in ALL samples with dysfunctional IL7R signaling (e. g., DND41 cells showing constitutive pathway activation due to IL7Rα mutations or NALM6 cells being absent of P-STAT5 induction upon IL7 stimulation). In this context, OSE-127-LALAPG did not impact leukemic engraftment as compared to control treatment, while OSE-127 significantly reduced leukemic burden, thereby substantiating that ADCP contributes to the anti-leukemic efficacy of OSE-127 (Figure 1E).
Finally, we conducted a phase2-like PDX overt leukemia study testing OSE-127 alone or in combination with Dexamethasone/Vincristine/PEG-Asparaginase chemotherapy employing PDX samples with high CD127 expression (6 BCP-ALL and 3 T-ALL-PDX samples with >50% CD127+ cells in flow cytometry analysis). OSE-127 alone significantly prolonged the survival of PDX mice in comparison to control treatment (MS 106d vs 79d, P=0.0071), which was comparable to the effect of chemotherapy (MS 106d vs 79d, P=0.0037). Importantly, the strongest effects were observed when combining OSE-127 with chemotherapy (MS 79d vs undefined, P=0.0003, Figure 1F).
Overall, we propose OSE-127 as a novel potential immunotherapeutic agent for the treatment of BCP-ALL and T-ALL, particularly in r/r disease and in combination with chemotherapy. Due to its dual mode of action comprising ADCP induction and IL7R-pathway blockade, OSE-127 could be efficacious in CD127+ ALL with and without IL7R pathway alterations.
L.L. and I.B. contributed equally to this work. N.P. and D.M.S. share senior authorship
Disclosures
Lenk:OSE Immunotherapeutics: Research Funding. Baccelli:OSE Immunotherapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Patents & Royalties. Corallo:OSE Immunotherapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Patents & Royalties. Taurelle:OSE Immunotherapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Patents & Royalties. Narbeburu:OSE Immunotherapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Patents & Royalties. Schrappe:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Research Funding; JazzPharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; SHIRE: Research Funding; SigmaTau: Research Funding. Poirier:OSE Immunotherapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Patents & Royalties. Schewe:OSE Immunotherapeutics: Research Funding.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.